JavaScript Evaluator
The JavaScript Evaluator processes data based on JavaScript code. Use the JavaScript processor to use JavaScript code to perform custom processing.
- Initialization script - Optional initialization script that sets up resources or connections required by the processor. The initialization script is run once when the pipeline starts.
- Main processing script - Main script that processes data. The main script is run for each record or each batch of data, based on the configured processing mode.
- Destroy script - Optional destroy script that closes any resources or connections opened by the processor. The destroy script is run once when the pipeline stops.
When you use a JavaScript Evaluator in a pipeline, the Data Collector passes a batch of data to the processor and converts the data to a scripting-friendly data structure for processing.
The JavaScript Evaluator supports Java version 8u40 and later and ECMAScript version 5.1. The processor runs on the Nashorn JavaScript engine.
The JavaScript Evaluator provides extensive sample code that you can use to develop your script. You can also call external Java code from the script.
Processing Mode
You can choose the processing mode that the JavaScript Evaluator uses to process the main script. You can use the same script in each processing mode. However, you should include error handling in the main script before you run in batch mode.
The JavaScript Evaluator provides the following processing modes for the main script:
- Record by Record
- The processor calls the script for each record. The processor passes the record to the script as a map and processes each record individually.
- Batch by Batch
- The processor calls the script for each batch. The processor passes the batch to the script as an array and processes the batch at one time.
JavaScript Scripting Objects
You can use different scripting objects in the JavaScript Evaluator, based on the type of script:
| Script Type | Valid Scripting Objects |
|---|---|
| Init | You can use the following scripting objects in the initialization
script:
|
| Main | You can use the following scripting objects in the main
script:
|
| Destroy | You can use the following scripting objects in the destroy
script:
|
${<parameter
name>}. The scripting objects work the same within each script type:
- records
- A collection of records to process. The records object includes different elements
based on the processing mode that you use:
- Record by Record - The records array includes one record element. A record
includes a single
valueelement. Thevalueelement contains the data for the record. - Batch by Batch - The records array includes all records in the batch.
- Record by Record - The records array includes one record element. A record
includes a single
- state
- An object to store information between invocations of the init, main, and destroy scripts. A state is a map object that includes a collection of key/value pairs. You can use the state object to cache data such as lookups, counters, or a connection to an external system.
- log
- An object to write messages to the log. Includes four methods:
info(),warn(),debug(), andtrace(). - output
- An object that writes the record to the output batch. Includes a
write(Record)method. - error
- An object that passes error records to the processor for error
handling. Includes a
write(Record, message)method.
- sdcFunctions
- An object that runs functions that evaluate or modify data. Includes the following methods:
Processing List-Map Data
In scripts that process list-map data, treat the data as maps.
List-Map is a Data Collector data type that allows you to use standard record functions to work with delimited data. When an origin reads delimited data, it generates List-Map fields by default.
The JavaScript Evaluator reads and passes list-map data. But to process data in a List-Map field, treat the field as a Map in the script.
Type Handling
Though JavaScript does not use type information when processing data, passing data to the rest of the pipeline requires data types. Note the following type information before you configure the remainder of the pipeline:
- Data type of null values
- The processor can associate null values with a data type. For example, if the JavaScript Evaluator assigns a null value to an Integer field, the field is returned to the pipeline as an integer with a null value.
- Date fields
- Use the String data type to create a new field to store a date with a specific format. For
example, the following sample code creates a new String field that stores the current
date using the format
YYYY-MM-dd:
// Define a date object to record the current date var date = new Date() for(var i = 0; i < records.length; i++) { try { // Create a string field to store the current date with the specified format records[i].value.date = date.getFullYear()+ "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDate() // Write record to the processor output output.write(records[i]); } catch (e) { // Send record to error error.write(records[i], e); } }
- Values retain their original type
- Values retain their original type regardless of whether the processor modifies the value.
Event Generation
You can use the JavaScript Evaluator to generate event records for an event stream. Enable event generation when you want the processor to generate an event record based on scripting logic.
As with any event record, you can pass events downstream to a destination for event storage or to any executor that can be configured to use the event. For more information about events and the event framework, see Dataflow Triggers Overview.
- On the General tab, select the Produce
Events property.
This enables the event output stream for use.
- In the script, include both of the following scripting objects:
- sdcFunctions.createEvent(String type, int version) - Creates an event
record with the specified event type and version number. You can create
a new event type or use an existing event type. Existing event types are
documented in other event-generating stages.
The event record contains no record fields. Generate record fields as needed.
- sdcFunctions.toEvent(Record) - Use to pass events to the event output stream.
- sdcFunctions.createEvent(String type, int version) - Creates an event
record with the specified event type and version number. You can create
a new event type or use an existing event type. Existing event types are
documented in other event-generating stages.
Working with Record Header Attributes
You can use the JavaScript Evaluator processor to read and update or create record header attributes.
Use a map when creating or updating a header attribute. If a header attribute exists, the processor updates the value, if it does not exist, the processor creates the attribute and sets it to the specified value.
All records include a set of read-only record header attributes that stages can update as they process the records. Error records also have their own set of read-only header attributes.
Some stages generate custom record header attributes that are meant to be used in particular ways. For example, the Oracle CDC Client origin specifies the operation type for a record in a record header attribute. And event-generating stages create a set of event header attributes for event records. For more information, see Record Header Attributes.
record.<header name>- Use to return the value of a read-only header attribute.record.attributes- Use to return a map of custom record header attributes, or to create or update a specific record header attribute.
Viewing Record Header Attributes
You can use data preview to view the record header attributes associated with a record at any given point in the pipeline. To view record header attributes, enable the Show Record/Field Header data preview property.
For example, the following image shows a record generated by the Directory origin in data preview.
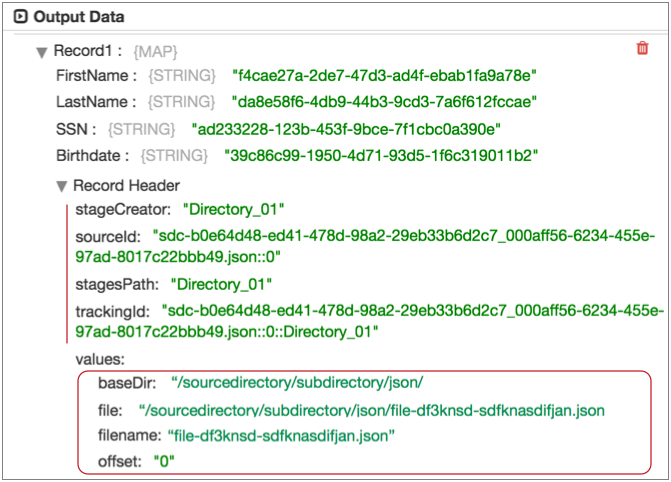
The "Record Header" list displays the set of
read-only internal attributes in the record at this point of the pipeline. You
can use the record.<header name> variable to return values for these
attributes.
The header attributes under "values" are the
attributes created by the Directory origin. You can use the
record.attributes variable to return or modify these attributes.
When you use the record.attributes variable to create a header
attribute, it displays in this location during data preview.
Accessing Whole File Format Records
In a pipeline that processes the whole file data format, you can use a JavaScript Evaluator to read the whole file data.
The processor can access the fileref field in a whole file record by creating an input stream using the getInputStream() API. For example, you might use the processor to read the file data in the fileref field and then create new records with the data. The processor can access the fileref field, but cannot modify information in the field.
input_stream = record.value['fileRef'].getInputStream()
input_stream.read()input_stream.close()Calling External Java Code
You can call external Java code from the JavaScript Evaluator. Simply install the external Java library to make it available to the JavaScript Evaluator. Then, call the external Java code from the script that you develop for the processor.
var <class name> = Java.type('<package>.<class name>');var DigestSHA3 = Java.type('org.bouncycastle.jcajce.provider.digest.SHA3.DigestSHA3');For more details, see the following StreamSets blog post: Calling External Java Code from Script Evaluators.
Configuring a JavaScript Evaluator
Configure a JavaScript Evaluator to use custom JavaScript in a pipeline.